assalamualaikum kali ini saya flazer kembali lagi post dengan tutorial
saya sendiri

kali ini saya memberi tutorial dengan nama membuat proxy server windows
karna saya lagi memakai os windows xp

jadi
saya buat tutorial nya dulu

mau tau manfaat dari proxy ini ???
Manfaat pakai Squid:
- Browsing semakin cepat (untuk situs yang sudah pernah dibuka)
- Ngirit bandwidth atau kuota pemakaian internet
- Expandable User (memperbanyak user yang boleh ikutan sharing
internet)
oke let's go kita saat nya beraksi :v

)
download dulu squid nya di sini :
here
oke sekarang apabila sudah di download copy ke
C:\ dan di extra
di sana

ntar apa bila sudah di extra buka folder
squid nya
c:\squid
Disana Anda akan menemukan beberapa file kongfigurasi. Ubah nama file
tersebut menjadi:
cachemgr.conf.default => cachemgr.conf
mime.conf.default => mime.conf
squid.conf.default => squid.conf
squid_radius_auth.conf.default => squid_radius_auth.conf
Konfigurasi Squid
Edit file squid.conf yang baru saja diubah namanya nanti cari bagian
Cari
http_port 3128 (
Pastikan tidak ada tanda # di depan baris tersebut. )
Cari
TAG: visible_hostname
Kurang lebih isinya sebagai berikut:
# TAG: visible_hostname
# If you want to present a special hostname in error messages, etc,
# define this. Otherwise, the return value of gethostname()
# will be used. If you have multiple caches in a cluster and
# get errors about IP-forwarding you must set them to have individual
# names with this setting.
#
#Default:
# none
Tambahkan
visible_hostname localhost di bawah tulisan #none.
Cari
TAG: http_access
Anda akan menemukan kode berikut:
# TAG: http_access
# Allowing or Denying access based on defined access lists
#
# Access to the HTTP port:
# http_access allow|deny [!]aclname …
#
# NOTE on default values:
#
# If there are no “access” lines present, the default is to deny
# the request.
#
# If none of the “access” lines cause a match, the default is the
# opposite of the last line in the list. If the last line was
# deny, the default is allow. Conversely, if the last line
# is allow, the default will be deny. For these reasons, it is a
# good idea to have an “deny all” or “allow all” entry at the end
# of your access lists to avoid potential confusion.
#
#Default:
# http_access deny all
#
#Recommended minimum configuration:
#
# Only allow cachemgr access from localhost
http_access allow manager localhost
http_access deny manager
# Deny requests to unknown ports
http_access deny !Safe_ports
# Deny CONNECT to other than SSL ports
http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports
#
# We strongly recommend the following be uncommented to protect innocent
# web applications running on the proxy server who think the only
# one who can access services on “localhost” is a local user
#http_access deny to_localhost
#
# INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS
# Example rule allowing access from your local networks.
# Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks
# from where browsing should be allowed
http_access allow localnet
Tambahkan
http_access allow localhost dibawah http_access allow
localnet.
Cari
TAG: dns_nameservers
Anda akan menemukan tulisan berikut:
# TAG: dns_nameservers
# Use this if you want to specify a list of DNS name servers
# (IP addresses) to use instead of those given in your
# /etc/resolv.conf file.
# On Windows platforms, if no value is specified here or in
# the /etc/resolv.conf file, the list of DNS name servers are
# taken from the Windows registry, both static and dynamic DHCP
# configurations are supported.
#
# Example: dns_nameservers 10.0.0.1 192.172.0.4
#
#Default:
# none
Tambahkan
dns_nameservers 208.67.222.222 208.67.220.220
dibawah #none (sesuaikan dengan DNS yang Anda dapat dari ISP. Contoh
disini saya menggunakan DNS Speedy)
Cari
TAG: cache_mgr
Kurang lebih Anda akan menemukan kode berikut:
# TAG: cache_mgr
# Email-address of local cache manager who will receive
# mail if the cache dies. The default is “webmaster”.
#
#Default:
# cache_mgr webmaster
Hilangkan tanda # di depan
cache_mgr webmaster dan silahkan ubah
nama webmaster menjadi nama atau alamat email Anda. Contoh:
cache_mgr
flazer
Cari
TAG: cache_dir
Lihat kode berikut:
# TAG: cache_dir
# Usage:
#
# cache_dir Type Directory-Name Fs-specific-data [options]
#
# You can specify multiple cache_dir lines to spread the
# cache among different disk partitions.
#
# Type specifies the kind of storage system to use. Only “ufs”
# is built by default. To enable any of the other storage systems
# see the –enable-storeio configure option.
#
# ‘Directory’ is a top-level directory where cache swap
# files will be stored. If you want to use an entire disk
# for caching, this can be the mount-point directory.
# The directory must exist and be writable by the Squid
# process. Squid will NOT create this directory for you.
# Only using COSS, a raw disk device or a stripe file can
# be specified, but the configuration of the “cache_swap_log”
# tag is mandatory.
#
# The ufs store type:
#
# “ufs” is the old well-known Squid storage format that has always
# been there.
#
# cache_dir ufs Directory-Name Mbytes L1 L2 [options]
#
# ‘Mbytes’ is the amount of disk space (MB) to use under this
# directory. The default is 100 MB. Change this to suit your
# configuration. Do NOT put the size of your disk drive here.
# Instead, if you want Squid to use the entire disk drive,
# subtract 20% and use that value.
#
# ‘Level-1? is the number of first-level subdirectories which
# will be created under the ‘Directory’. The default is 16.
#
# ‘Level-2? is the number of second-level subdirectories which
# will be created under each first-level directory. The default
# is 256.
#
# The aufs store type:
#
# “aufs” uses the same storage format as “ufs”, utilizing
# POSIX-threads to avoid blocking the main Squid process on
# disk-I/O. This was formerly known in Squid as async-io.
#
# cache_dir aufs Directory-Name Mbytes L1 L2 [options]
#
# see argument descriptions under ufs above
#
# The diskd store type:
#
# “diskd” uses the same storage format as “ufs”, utilizing a
# separate process to avoid blocking the main Squid process on
# disk-I/O.
#
# cache_dir diskd Directory-Name Mbytes L1 L2 [options] [Q1=n] [Q2=n]
#
# see argument descriptions under ufs above
#
# Q1 specifies the number of unacknowledged I/O requests when Squid
# stops opening new files. If this many messages are in the queues,
# Squid won’t open new files. Default is 64
#
# Q2 specifies the number of unacknowledged messages when Squid
# starts blocking. If this many messages are in the queues,
# Squid blocks until it receives some replies. Default is 72
#
# When Q1 < Q2 (the default), the cache directory is optimized
# for lower response time at the expense of a decrease in hit
# ratio. If Q1 > Q2, the cache directory is optimized for
# higher hit ratio at the expense of an increase in response
# time.
#
# The coss store type:
#
# block-size=n defines the “block size” for COSS cache_dir’s.
# Squid uses file numbers as block numbers. Since file numbers
# are limited to 24 bits, the block size determines the maximum
# size of the COSS partition. The default is 512 bytes, which
# leads to a maximum cache_dir size of 512<<24, or 8 GB. Note
# you should not change the COSS block size after Squid
# has written some objects to the cache_dir.
#
# overwrite-percent=n defines the percentage of disk that COSS
# must write to before a given object will be moved to the
# current stripe. A value of “n” closer to 100 will cause COSS
# to waste less disk space by having multiple copies of an object
# on disk, but will increase the chances of overwriting a popular
# object as COSS overwrites stripes. A value of “n” close to 0
# will cause COSS to keep all current objects in the current COSS
# stripe at the expense of the hit rate. The default value of 50
# will allow any given object to be stored on disk a maximum of
# 2 times.
#
# max-stripe-waste=n defines the maximum amount of space that COSS
# will waste in a given stripe (in bytes). When COSS writes data
# to disk, it will potentially waste up to “max-size” worth of disk
# space for each 1MB of data written. If “max-size” is set to a
# large value (ie >256k), this could potentially result in large
# amounts of wasted disk space. Setting this value to a lower value
# (ie 64k or 32k) will result in a COSS disk refusing to cache
# larger objects until the COSS stripe has been filled to within
# “max-stripe-waste” of the maximum size (1MB).
#
# membufs=n defines the number of “memory-only” stripes that COSS
# will use. When an cache hit is performed on a COSS stripe before
# COSS has reached the overwrite-percent value for that object,
# COSS will use a series of memory buffers to hold the object in
# while the data is sent to the client. This will define the maximum
# number of memory-only buffers that COSS will use. The default value
# is 10, which will use a maximum of 10MB of memory for buffers.
#
# maxfullbufs=n defines the maximum number of stripes a COSS partition
# will have in memory waiting to be freed (either because the disk is
# under load and the stripe is unwritten, or because clients are still
# transferring data from objects using the memory). In order to try
# and maintain a good hit rate under load, COSS will reserve the last
# 2 full stripes for object hits. (ie a COSS cache_dir will reject
# new objects when the number of full stripes is 2 less than
maxfullbufs)
#
# The null store type:
#
# no options are allowed or required
#
# Common options:
#
# no-store, no new objects should be stored to this cache_dir
#
# min-size=n, refers to the min object size this storedir will accept.
# It’s used to restrict a storedir to only store large objects
# (e.g. aufs) while other storedirs are optimized for smaller objects
# (e.g. COSS). Defaults to 0.
#
# max-size=n, refers to the max object size this storedir supports.
# It is used to initially choose the storedir to dump the object.
# Note: To make optimal use of the max-size limits you should order
# the cache_dir lines with the smallest max-size value first and the
# ones with no max-size specification last.
#
# Note that for coss, max-size must be less than COSS_MEMBUF_SZ
# (hard coded at 1 MB).
#
#Default:
# cache_dir ufs c:/squid/var/cache 100 16 256
Hilangkan tanda # di depan
cache_dir ufs c:/squid/var/cache 100 16
256. Ubah nilai 100. Contoh:
cache_dir ufs c:/squid/var/cache
30720 16 256 (saya memasukkan nilai 30720, artinya kapasitas
harddisk untuk cache squid sebesar 30720 MB atau sekitar 30 GB)
Cari
TAG: cache_mem
Lihat kode berikut:
# TAG: cache_mem (bytes)
# NOTE: THIS PARAMETER DOES NOT SPECIFY THE MAXIMUM PROCESS SIZE.
# IT ONLY PLACES A LIMIT ON HOW MUCH ADDITIONAL MEMORY SQUID WILL
# USE AS A MEMORY CACHE OF OBJECTS. SQUID USES MEMORY FOR OTHER
# THINGS AS WELL. SEE THE SQUID FAQ SECTION 8 FOR DETAILS.
#
# ‘cache_mem’ specifies the ideal amount of memory to be used
# for:
# * In-Transit objects
# * Hot Objects
# * Negative-Cached objects
#
# Data for these objects are stored in 4 KB blocks. This
# parameter specifies the ideal upper limit on the total size of
# 4 KB blocks allocated. In-Transit objects take the highest
# priority.
#
# In-transit objects have priority over the others. When
# additional space is needed for incoming data, negative-cached
# and hot objects will be released. In other words, the
# negative-cached and hot objects will fill up any unused space
# not needed for in-transit objects.
#
# If circumstances require, this limit will be exceeded.
# Specifically, if your incoming request rate requires more than
# ‘cache_mem’ of memory to hold in-transit objects, Squid will
# exceed this limit to satisfy the new requests. When the load
# decreases, blocks will be freed until the high-water mark is
# reached. Thereafter, blocks will be used to store hot
# objects.
#
#Default:
# cache_mem 8 MB
Hilangkan tanda # di depan
cache_mem 8 MB, dan ubah sizenya.
Sebaiknya 1/3 dari size RAM komputer Anda. Contoh:
cache_mem 1024 MB (saya
menggunakan 1024 MB atau sekitar 1 GB untuk squid proxy)Cari
TAG:
minimum_object_size
Lihat kode berikut:
# TAG: minimum_object_size (bytes)
# Objects smaller than this size will NOT be saved on disk. The
# value is specified in kilobytes, and the default is 0 KB, which
#means there is no minimum.
#
#Default:
# minimum_object_size 0 KB
Hilangkan tanda # di depan
minimum_object_size 0 KB. Sesuaikan
sizenya. Contoh:
minimum_object_size 1 KB. Artinya, minimal file
yang akan disimpan ke dalam harddisk sebesar 1 KB.
Cari
TAG: maximum_object_size
Lihat kode berikut:
# TAG: maximum_object_size (bytes)
# Objects larger than this size will NOT be saved on disk. The
# value is specified in kilobytes, and the default is 4MB. If
# you wish to get a high BYTES hit ratio, you should probably
# increase this (one 32 MB object hit counts for 3200 10KB
# hits). If you wish to increase speed more than your want to
# save bandwidth you should leave this low.
#
# NOTE: if using the LFUDA replacement policy you should increase
# this value to maximize the byte hit rate improvement of LFUDA!
# See replacement_policy below for a discussion of this policy.
#
#Default:
# maximum_object_size 4096 KB
Hilangkan tanda # di depan
maximum_object_size 4096 KB. Sesuaikan
size untuk maksimal file yang akan disimpan ke dalam harddisk.
Cari TAG:
maximum_object_size_in_memory
Lihat kode berikut:
# TAG: maximum_object_size_in_memory (bytes)
# Objects greater than this size will not be attempted to kept in
# the memory cache. This should be set high enough to keep objects
# accessed frequently in memory to improve performance whilst low
# enough to keep larger objects from hoarding cache_mem.
#
#Default:
# maximum_object_size_in_memory 8 KB
Hilangkan tanda # di depan
maximum_object_size_in_memory 8 KB.
Sesuaikan nilai untuk maksimal file yang tersimpan sementara di memory.
Simpan file konfigurasi yang telah kita buat diatas. Jalankan command
prompt. Klik
Start?Run?ketik cmd
Masuk ke direktori C:\squid\sbin dengan mengetikan perintah
berikut
cd C:\squid\sbin
Ketik
squid –z [ enter]. Untuk membuat direktori swap/cache.
Ketik
squid –d 1 –D [enter]. Option “-d 1”
digunakan untuk masuk ke debug level (untuk diagnosa saja) dan option
“-D” digunakan untuk membypass pengecekan DNS, berguna jika anda belum
terkoneksi ke internet.
Ketik
squid –i [enter]. Untuk memasukkan squid ke dalam service
windows.
Ketik
squid –O –D [enter]. Untuk memasukkan parameter –D ke
registry ketika service dijalankan.
Jalankan service dengan cara
Start => Run => services.msc =>
cari service dengan nama squid kemudian klik kanan pilih Start.
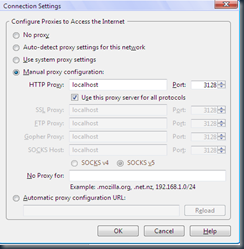
oke sekarang kita buka browser kita seting

seperti gambar di bawah ini
Selesai, rasakan bedanya
Untuk uninstal squid:
- Masuk ke Start >> Run >> CMD
- Muncul command terus ketik cd C:\squid\sbin (enter)
- squid -r (enter)
Normal lagi deh internet kamu kayak semula, jangan lupa setting
ulang network browser kamu ke direct “No
proxy“Eittsss… belum… masih ada satu langkah lagi. Kita jalankan LUSCA Head r14809 terlebih dahulu :